Introduction: Why Understanding the Architecture Matters
To effectively secure a Large Language Model (LLM), we need to first understand its internal architecture. LLM systems are composed of several interconnected layers, each with distinct functions and potential vulnerabilities. In this part, we will dissect the architecture layer by layer, providing a clear view of how data flows through an LLM system.
1. AI Model Layer: The Neural Network Backbone
The AI Model Layer contains the neural network itself — the engine that powers the LLM. This layer is where data gets processed based on the parameters and weights established during training.

This layer is the most computation-intensive and is where the model’s logic resides.Key security concerns: Data poisoning, model theft, and adversarial attacks.
2. Infrastructure/Ops Layer: The Foundation
At the core of every LLM system lies its infrastructure, including servers, databases, storage systems, and network configurations.
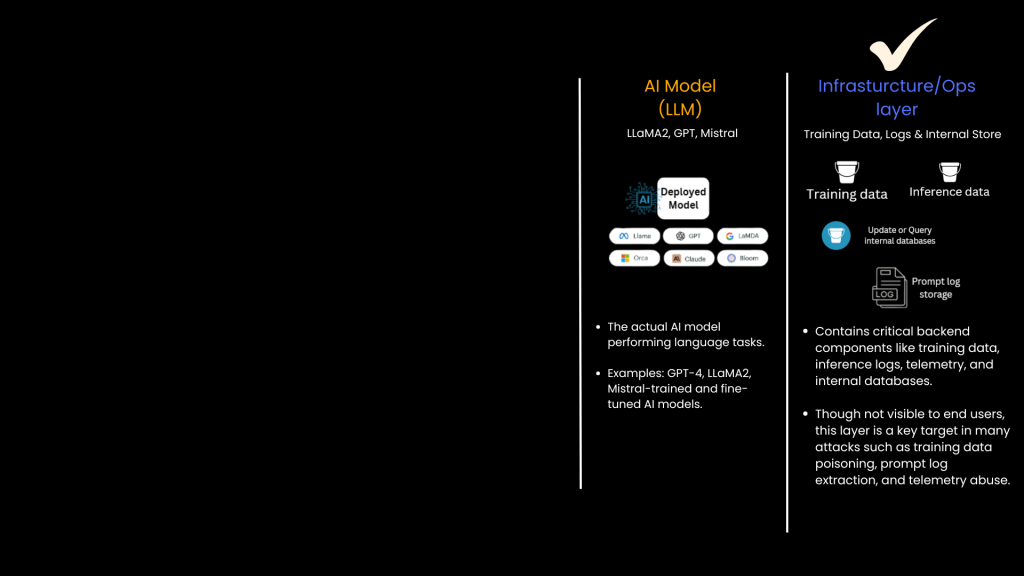
- The infrastructure layer handles data storage, processing power, and network communications.
- Potential security risks: Network breaches, data storage vulnerabilities, and server misconfigurations.
3. LLM Processing Layer: The Intelligence Unit
Once the user input reaches the processing layer, it is passed to the LLM processing unit. This unit applies the model’s neural network to generate a response based on training data.
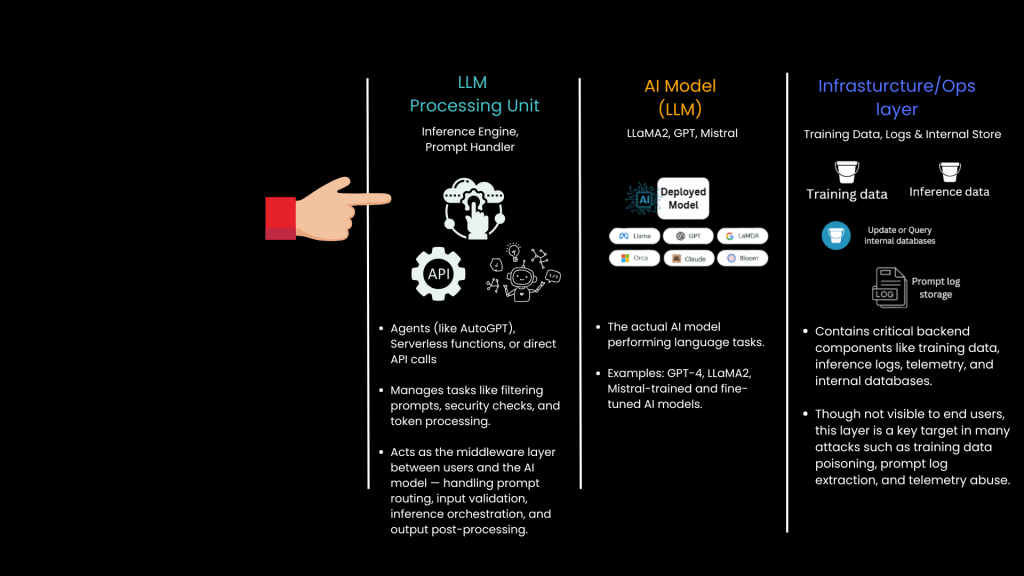
- The processing unit is the heart of the LLM system. It interprets user prompts, processes them using its neural network, and formulates responses.
- Potential vulnerabilities: Prompt injection attacks, data manipulation, and model inference attacks.
4. Integration Layer: Connecting the Components
The Integration Layer connects the LLM with external data sources, APIs, and third-party services. This layer ensures that data flows smoothly between different parts of the system.

- This layer is crucial for expanding LLM functionality through external APIs, databases, and third-party services.
- Vulnerabilities include API misconfigurations, unauthorized access, and data leakage.
5. Application Layer: The User Interface
The Application Layer is the visible part of the LLM system that interacts directly with users. It could be a chatbot, a web interface, or a third-party integration.
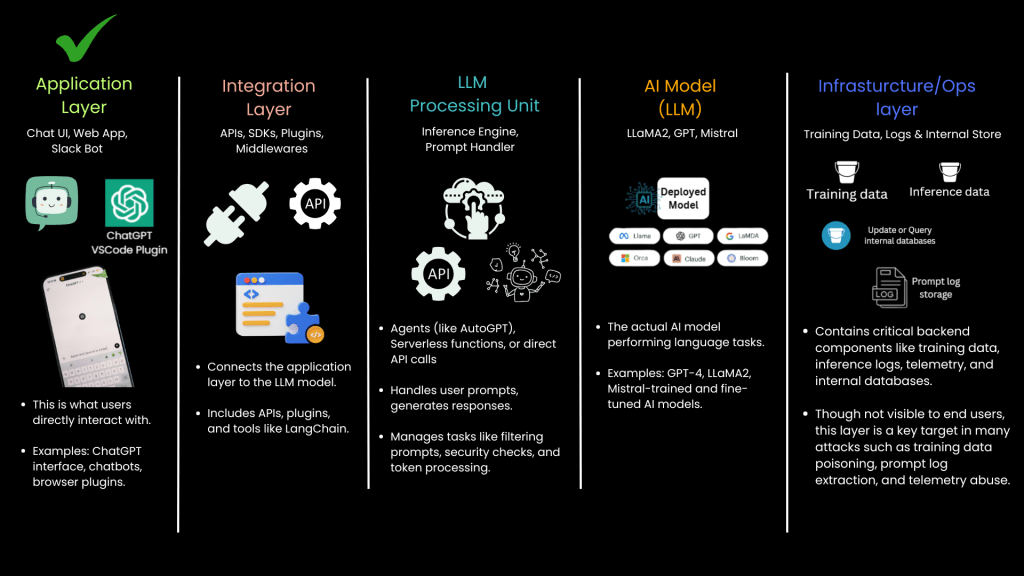
- This layer is responsible for collecting user inputs, formatting them, and sending them to the LLM processing unit.
- Key security considerations include input validation, authentication, and preventing unauthorized access.
That’s all for this part where we broke down the internal architecture of Large Language Models, dissecting each layer from data ingestion to inference.
In the next part of this series, we will explore the attack surfaces in LLM systems — identifying how each layer we discussed can be targeted, misconfigured, or exploited by attackers. We will also dive into real-world case studies that reveal how vulnerabilities in APIs, training data, and log storage can expose sensitive information and compromise AI systems.



Leave a comment